Main Points
- Margin trading involves trading on the spot market with borrowed funds. Traders pay a fixed hourly rate for using these funds.
- Futures trading involves trading contracts based on the price fluctuations of an asset. Users trade these contracts by depositing collateral and paying or receiving funding rates for open positions every eight hours.
- The main difference between futures trading and margin trading is the maximum leverage ratio: up to 125x for futures trading compared to up to 10x for margin trading.
What is leverage?
Leverage, also known as credit leverage, is a mechanism that allows traders to open positions with a larger amount than what is available in their account. It enables traders to increase potential profits through long positions and profit from price decreases through short selling.
The leverage ratio represents the ratio of the position size with borrowed assets to the funds allocated by the trader. For example, with a leverage ratio of 10x, a user with a $1000 deposit can buy or sell assets worth $10,000.
Using leverage not only increases potential profits but also potential losses. With 10x leverage, for example, a trader can lose their entire margin if the asset’s prices drop by 10%.
What is margin trading?
Margin trading is trading with credit leverage on the spot market. Traders buy and sell cryptocurrencies, which can then be withdrawn to external wallets. To open a position, traders borrow additional funds against margin collateral. The trading platform or the investors of its investment products act as lenders.
What is futures trading?
Futures trading involves trading derivative contracts (futures) where parties agree to buy or sell an asset in the future at a predetermined price. To open a position in the futures market, a trader needs to provide collateral that covers the potential loss. Cryptocurrency exchanges offer perpetual non-deliverable futures: buyers and sellers make bets on the price changes of an asset and settle in stablecoins upon contract completion. They cannot request physical delivery of cryptocurrencies or settle contracts in cryptocurrencies.
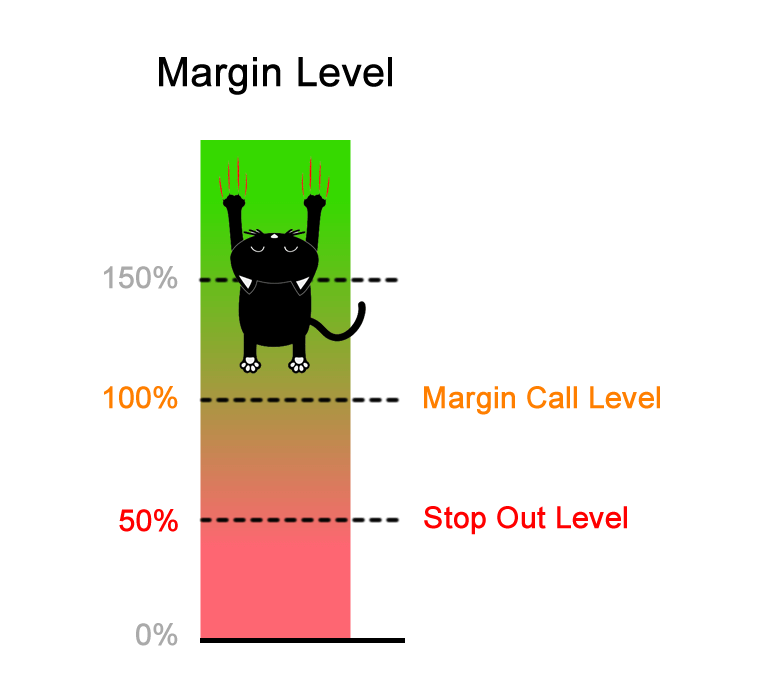
What is a margin call and liquidation in leveraged trading?
A margin call is a notification from the exchange requesting additional margin or collateral for a losing position. For example, Poloniex sends a margin call to a trader when the loss reaches 75% of the margin.
When holding positions on both markets, traders additionally pay:
- n margin trading, traders are charged an hourly interest rate for using borrowed assets. The average rate for Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Tether ranges from 3.65% to 1.27% per year, depending on the trading volume.
- In futures trading, financing rates are applied every eight hours. If the contract is trading at a lower price than the spot market, buyers pay sellers, and vice versa. For instance, the total financing rate for holders of long positions in BTCUSDTPERP on Poloniex in April was 0.754% or 9.05% per year.
Here are the differences between margin trading and futures trading:
- Margin Trading:
- Conducted on the spot market, while futures trading occurs on the cryptocurrency derivatives market.
- In margin trading, buyers have the option to withdraw assets to external wallets, whereas in futures trading, this is not possible.
- Maximum leverage in margin trading is up to 3x.
- Futures Trading:
- Takes place on the cryptocurrency derivatives market.
- Maximum leverage in futures trading is higher, often up to 100x.
- Position size limitations in margin trading can go up to 120 BTC, whereas in futures trading, it is typically limited to 25 BTC.
- There are more futures contracts available compared to trading pairs in margin trading. For example, on Poloniex, there may be 38 futures contracts available while only 12 cryptocurrencies are available for margin trading.
- Due to the higher leverage offered in futures trading, the market tends to be more volatile. This increased volatility raises the risk of liquidation and stop-order position closures.
- In margin trading, two cryptocurrencies are used for long purchases and short sales. In contrast, in futures trading, traders provide collateral in a single currency, regardless of the position’s direction.
For beginners, margin trading is generally more suitable. It carries fewer financial risks due to several factors:
- Low leverage of up to 3x, reducing the potential for large losses.
- The spot market tends to have lower volatility compared to futures trading.
- There is a fixed hourly rate for using the funds, allowing for better cost predictability.
- Trading is limited to the most popular and liquid cryptocurrencies, which are generally more stable.
Futures trading, on the other hand, allows for potentially higher profits but comes with higher risks:
- Liquidation risk when using high leverage, such as up to 100x, which can result in significant losses.
- The possibility of stop-loss orders being triggered unexpectedly when trading contracts with low liquidity.
- Slippage when executing market orders during periods of high volatility.
Futures trading is more suitable for traders who are already experienced in managing capital and can take advantage of market volatility and high leverage effectively. Beginners may find margin trading a more suitable option to gain familiarity with trading concepts and minimize risks.
You can try all types of trading on the most popular and renowned cryptocurrency exchange in the world, Binance.

